Dr. Eadie’s Published Research
A unique case of glaucoma associated with heterotopic bone formation in the anterior chamber angle [Nov 10, 2023]
Fig. 1. (A) Anterior view of the patient’s right eye, showing inferior and temporal deposits of white material (yellow arrows). (B) Gonioscopic view of the materials in the anterior chamber angle. (C) Ultrasound biomicroscopy image highlighting the position of the deposits over the anterior chamber angle. (D) Surgical removal of the deposit with microforceps.
Ab interno trabeculectomy revision with 5-flourouracil for failed trabeculectomy in advanced glaucoma: 3-year outcomes [Jan 27, 2024]
Fig. 1. Mean intraocular pressure (IOP; with 95% CI) and number of topical IOP-lowering drops (with 95% CIs) after ab interno revision. Last IOP measurement before any subsequent additional glaucoma surgery (n = 7) was carried forward with the remaining number of eyes included in parentheses.
Medications for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder associated with increased risk of developing glaucoma [May 26, 2024]
CONCLUSIONS: Use of amphetamines and atomoxetine had a higher risk for ACG, while use of methylphenidate was associated with a higher risk for OAG. Given the prevalence of ADHD medication use (medically and recreationally), our current data on Their associated risk of glaucoma have profound public health implications.
Increased risk of pigmentary degeneration of the iris and pigmentary glaucoma with fluoroquinolone antibiotics [July 29, 2024]
CONCLUSIONS: The study findings suggest that patients using topical moxifloxacin may have increased risk of developing pigmentary degeneration of the iris and pigmentary glaucoma although the absolute increase was low. Future studies are needed to confirm this association.
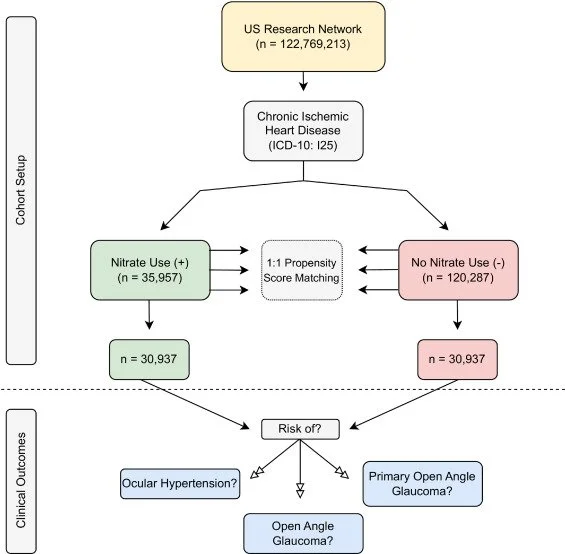
Association Between Chronic Oral Nitrate Use and the Risk of Ocular Hypertension and Open-Angle Glaucoma [July 14, 2025]
CONCLUSIONS: The use of oral nitrates was associated with a reduced risk of OAG and POAG over long-term follow-up, while no effect was observed on OHT development.
Luminance and thresholding limitations of virtual reality headsets for visual field testing [September 19, 2025]
CONCLUSIONS: Commercially available VR devices do not meet luminance requirements or threshold sensitivities for visual field testing. Current VR technology is not designed—nor has the capacity—to threshold at mid-to-low dB ranges, which limits accuracy in diagnosing and monitoring defects seen in glaucoma.
Translational Relevance: This study highlights the technical limitations of current commercially available VR devices for visual field testing and significant variables in evaluating luminance performance in these devices.
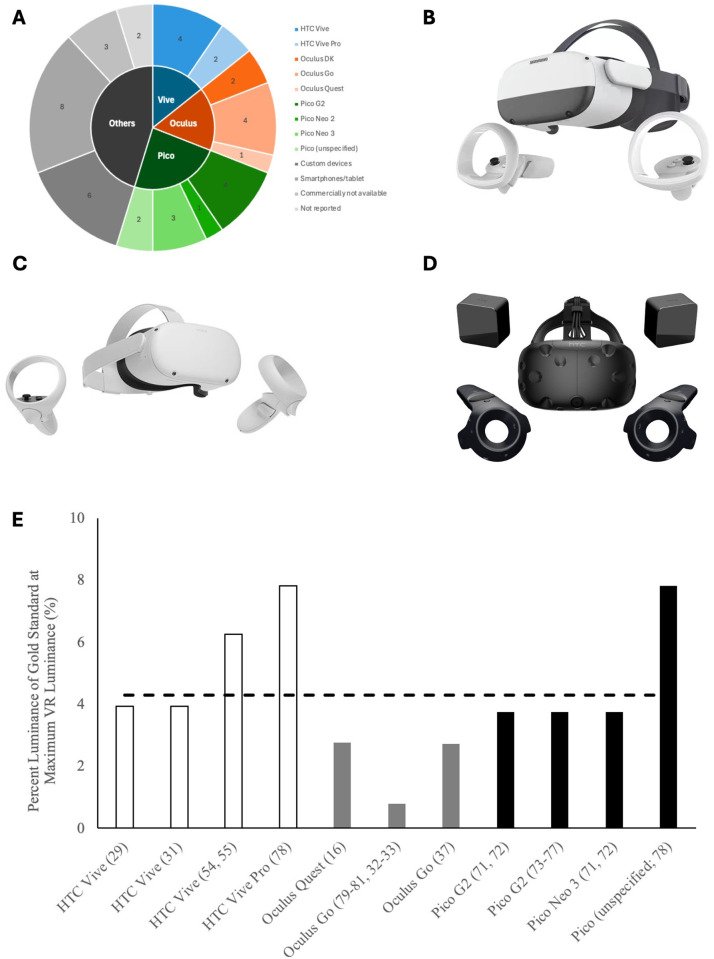
Fig 1. Review of VR devices used for visual field testing in the literature. (A) Type of VR devices used for visual field testing in the literature. Three most commonly used headsets: (B) Pico Neo 3, (C) Oculus Quest 2, and (D) HTC Vive. (E) Percent maximum luminance of VR devices compared to that of conventional perimeters.